Uncategorised
8 Professional Engraving Techniques That Transform Ordinary Items Into Treasured Keepsakes
From ancient civilisations carving their stories into stone to modern laser systems creating intricate designs on metal, engraving has evolved into a sophisticated craft that combines artistry with precision technology. Whether you’re seeking to personalise a wedding gift, create corporate awards, or preserve family memories, understanding the different types of engraving techniques available can help you choose the perfect method for your project. Each technique offers unique advantages, from the deep, tactile impressions of traditional hand engraving to the precise detail possible with modern laser systems. The choice between methods depends on factors including your material, desired aesthetic, budget, and timeframe.
Traditional Hand Engraving: The Timeless Art of Personalisation
Hand engraving represents the oldest and most traditional form of engraving, where skilled artisans use specialised tools called gravers or burins to cut designs directly into materials. This technique requires years of training to master, as engravers must develop steady hands, artistic vision, and deep understanding of how different materials respond to cutting tools.

The process involves holding the graver at specific angles and applying controlled pressure to create lines of varying depths and widths. Master engravers can create everything from simple text to intricate scrollwork, monograms, and detailed illustrations. The beauty of hand engraving lies in its organic nature – no two pieces are identical, and the subtle variations in line weight and depth create character that machine processes cannot replicate.
Materials well-suited for hand engraving include precious metals like gold and silver, brass, copper, and certain types of steel. The technique excels on curved surfaces such as jewellery, watches, and ceremonial items where the engraver can adapt their approach to the contours of the piece. Traditional engraving techniques have been documented throughout history, from ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs to Renaissance artwork.
Laser Engraving: Precision Meets Modern Technology
Laser engraving has revolutionised the industry by offering unprecedented precision, consistency, and versatility. This computer-controlled process uses focused laser beams to vaporise material surfaces, creating permanent marks without physical contact between tool and workpiece.
The technology operates by directing high-intensity light beams that heat the material to its vaporisation point, effectively removing microscopic layers to create the desired pattern. Different laser types serve various applications: CO2 lasers work excellently on organic materials like wood and leather, while fiber lasers excel with metals and plastics.
Key Advantages of Laser Engraving
- Exceptional detail reproduction, capable of creating intricate designs with fine lines
- Consistent results across large production runs
- No tool wear, eliminating the need for replacement cutting implements
- Ability to engrave complex graphics, photographs, and detailed logos
- Fast processing times for high-volume projects
Laser engraving works effectively on materials including stainless steel, aluminium, titanium, acrylic, wood, leather, glass, and many plastics. The technique proves particularly valuable for corporate awards, promotional items, and products requiring precise text or logo reproduction.
Rotary Engraving: Mechanical Precision for Professional Results
Rotary engraving employs computer-controlled cutting tools that physically remove material through mechanical action. Unlike laser systems that vaporise material, rotary engraving uses diamond-tipped or carbide cutting bits that carve into surfaces, creating tactile impressions with varying depths.
The process begins with digital design files that control the movement of cutting tools across the material surface. Operators can adjust cutting depth, speed, and tool selection to achieve different effects, from shallow surface marking to deep relief carving. This versatility makes rotary engraving suitable for both decorative applications and functional marking requirements.
Materials compatible with rotary engraving include brass, aluminium, stainless steel, plastics, laminates, and composite materials. The technique excels for applications requiring filled lettering, where contrasting colours enhance readability. Many trophy shops and sign manufacturers prefer rotary engraving for its ability to create professional-looking nameplates and signage with crisp, clean edges.
Chemical Etching: Creating Intricate Patterns Through Controlled Corrosion
Chemical etching, also known as acid etching, uses controlled chemical reactions to remove material selectively from surfaces. This process involves applying acid-resistant masks to protect certain areas while exposing others to etching solutions that gradually dissolve the unprotected material.
The technique begins with thorough surface preparation, followed by application of resist materials such as specialty films or photosensitive coatings. Desired patterns are transferred onto the resist layer through photolithographic processes or direct application methods. Once the resist pattern is established, the piece undergoes controlled exposure to etching chemicals under carefully monitored conditions.
Applications and Material Compatibility
Chemical etching proves particularly effective for creating uniform depth patterns across large surfaces, making it ideal for architectural panels, industrial nameplates, and decorative screens. The process works well with stainless steel, aluminium, brass, copper, and certain specialty alloys. Chemical etching processes have been refined over centuries, originating from printmaking techniques developed in the 16th century.
One significant advantage of chemical etching is its ability to process multiple pieces simultaneously, making it cost-effective for medium to large production runs. The technique also maintains consistent depth across complex geometries, unlike mechanical processes that may struggle with intricate internal features.
Diamond Drag Engraving: Precision Without Heat or Chemicals
Diamond drag engraving utilizes industrial diamonds mounted in specialised holders to scratch precise patterns into material surfaces. This mechanical process creates permanent marks through controlled pressure rather than heat or chemical reactions, making it suitable for heat-sensitive materials.
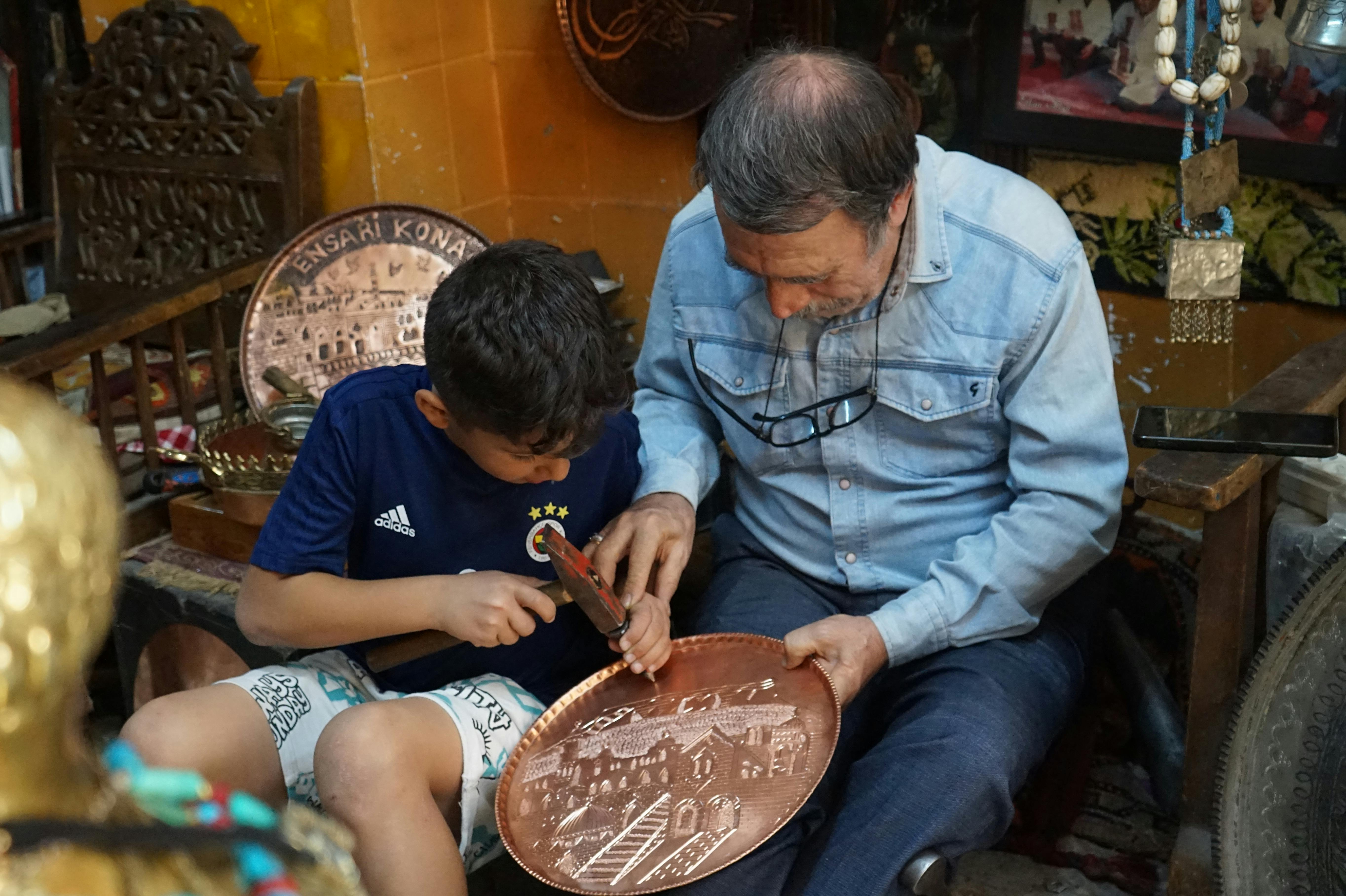

The diamond stylus follows computer-controlled paths across the workpiece surface, applying consistent pressure to create uniform line widths and depths. The process can produce both single-line text and filled areas through overlapping passes, though it typically works best for applications requiring clean, professional marking rather than artistic detail.
Materials well-suited for diamond drag engraving include anodized aluminium, painted metals, laminates, and certain plastics. The technique proves particularly valuable for control panels, instrument faces, and applications where heat-affected zones from laser processing might compromise material properties or nearby components.
Impact Engraving: Fast, Economical Marking Solutions
Impact engraving, also called dot peen marking, creates permanent impressions through rapid, controlled impacts against the material surface. The system uses pneumatic or electromagnetic actuators to drive hardened steel or carbide styluses into workpieces, creating series of overlapping dots that form characters and patterns.
This marking method excels for industrial applications requiring traceability marking, serial numbers, and date codes. The process operates at high speeds, making it economical for high-volume production environments. Impact systems can mark directly onto finished parts without requiring special surface preparation or post-processing steps.
The technique works effectively on virtually all metals, including hardened steel, and many hard plastics. Manufacturing standards organizations often recommend impact marking for applications requiring permanent traceability in aerospace, automotive, and medical device industries.
Choosing the Right Engraving Technique for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate engraving method requires careful consideration of multiple factors that influence both the process and final results. Material composition serves as the primary determining factor, as different techniques work optimally with specific material types.

Material Considerations
- Metals: Hand engraving and laser systems work well for precious metals, while impact engraving suits industrial applications
- Plastics: Laser and rotary engraving typically provide the best results
- Glass: Laser engraving or chemical etching offer the most control
- Wood and organic materials: Laser engraving provides excellent detail with minimal material distortion
Project volume significantly impacts technique selection. Hand engraving suits one-off custom pieces and high-value items where uniqueness adds value. Laser and rotary systems excel for medium volumes, while chemical etching becomes cost-effective for large production runs requiring identical results.
Design complexity also influences method choice. Simple text and basic logos work well with any technique, while intricate artwork or photographic reproduction requires laser engraving capabilities. Consider whether the application requires filled lettering, specific depth requirements, or particular aesthetic qualities that certain techniques provide better than others.
Future Trends in Engraving Technology
The engraving industry continues evolving with technological advances that improve precision, expand material compatibility, and increase processing speeds. Ultrafast laser systems now enable processing of materials previously considered difficult to engrave, while improved software interfaces make complex design creation more accessible.
Hybrid systems combining multiple engraving technologies in single machines offer increased flexibility for shops handling diverse projects. These integrated solutions allow operators to select optimal processes for specific applications without requiring multiple specialized machines.
Environmental considerations increasingly influence technique selection, with water-based chemical etching solutions and improved laser efficiency reducing environmental impact while maintaining processing quality.
Whether you’re preserving memories through personalised gifts or marking industrial components for traceability, understanding different types of engraving techniques empowers you to make informed decisions that ensure optimal results. Professional engraving services can guide you through technique selection, helping match your specific requirements with the most appropriate process for achieving your desired outcome.

